Project management teams use Scrum, a popular agile approach that improves productivity and cooperation during project planning and execution. This blog will explore Scrum’s role in sprint-based project management, namely its concepts, benefits, and link to Project Management Training.
Before we discuss Scrum further, let’s first clarify the basic question: What Are Sprints in Project Management?
What Are Sprints in Project Management?
Before implementing Scrum, it is important to understand project management sprints. Sprints are short time-boxed periods of a set of tasks or goals that have to be accomplished within it. Usually taking two to four weeks, sprints represent an organized way for teams to go about projects and focus on tiny increments. At its core, this iterative cycle is what defines agile practices, and it is also the foundation of Scrum as a distinct project management methodology.
Since project management training is so critical, aspiring project management experts; together with their teams must know about what constitutes Sprinting. During the tenure of these bounded-timed iterations, scrum leverages its true power in giving the rhythms of projects a disciplined and dynamic consistency.
The Pillars of Scrum
Adaptation, Transparency, and Inspection
One of Scrum’s foundations is its emphasis on adaptability, openness, and scrutiny. These three rules guarantee that everyone on the team knows the project’s present status, any potential impediments, and the group’s sprint objectives. Teams may continuously enhance productivity and adapt to changing project needs by doing routine inspections and altering procedures.
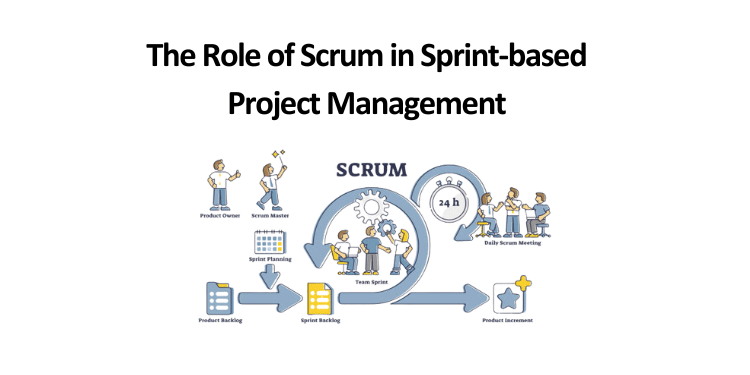
Scrum Roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team
Scrum provides clear roles with specific duties within a project team. All the customers like to make sure the quality of delivery value after each sprint which checked by the product owner after the end of each sprint. As a facilitator, the Scrum Master breaks down barriers and promotes a cooperative and effective atmosphere. With their knowledge and commitment, the talented members of the Development Team make the idea a reality.
Artefacts: Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment
Scrum uses various artefacts to keep things organised and clear. The Product Owner prioritises a dynamic list of upgrades and improvements called the Product Backlog. The Sprint Backlog gives the team a concrete strategy by listing the tasks that must be accomplished within a sprint. The total number of tasks finished after a sprint is called the Increment, representing a potentially shippable product increment.
Benefits of Scrum in Sprint-based Project Management
Enhanced Flexibility and Adaptability
Scrum’s iterative structure, which emphasises brief, well-defined sprints, gives teams unmatched flexibility. This flexibility is especially useful in fast-paced businesses where needs could alter drastically. Scrum enables teams to change course quickly, modifying plans and priorities as necessary and strengthening the project management framework.
Improved Collaboration and Communication
Scrum places a strong emphasis on teamwork, dismantling silos, and encouraging candid communication. A quick but essential component of the Scrum framework, daily Scrum meetings ensure that team members are in agreement about objectives, progress, and any obstacles. This ongoing communication fosters a sense of shared accountability and ownership, which is crucial for the success of project outputs.
Continuous Delivery of Value
Scrum helps ensure that stakeholders receive value continuously by breaking work into small sprints. After each sprint, a potentially shippable product increment is shown, enabling quick validation and feedback. This iterative methodology maintains stakeholder engagement throughout the project, and the final delivery closely matches their changing needs.
Scrum and Project Management Training
There is an increasing need for qualified personnel as project management advances. This leads us to the point where project management training and Scrum work hand in hand. Those interested in improving their project management abilities should embrace the Scrum principles.
Integrating Scrum into Project Management Training
Project management training programs that integrate Scrum give participants a flexible and pragmatic approach to project execution. With a unique perspective and practical knowledge from Scrum simulations and real-world implementations, trainees can confidently handle challenging projects.
Certifications for Proficiency
Given Scrum’s importance in contemporary project management, several certifications are offered to verify competence. In the industry, certifications like the Professional Scrum Master (PSM) and Certified Scrum Master (CSM) are highly regarded for formally acknowledging a person’s capacity to use Scrum concepts.
Conclusion
Scrum is a shining example of innovation in project management, where flexibility and productivity are critical. By adopting Scrum’s guiding principles, teams may handle contemporary projects with purpose and agility. The combination of Scrum and project management training improves individual competencies and advances the field of project management.
In sprint-based project management, Scrum’s influence is expected to grow in the future, influencing how teams work together, develop new ideas, and produce outstanding outcomes.