Engineering involves a lot of transportation and movement of goods with the actual science beneath the process. When a material is loaded, it definitely changes shape.
Along with it, a deformation also takes place that can be measured with the help of accurate calculations. It is called yield stress measurement, and it is the only way by which you can actually understand the stress load and the position of the material with respect to the same.
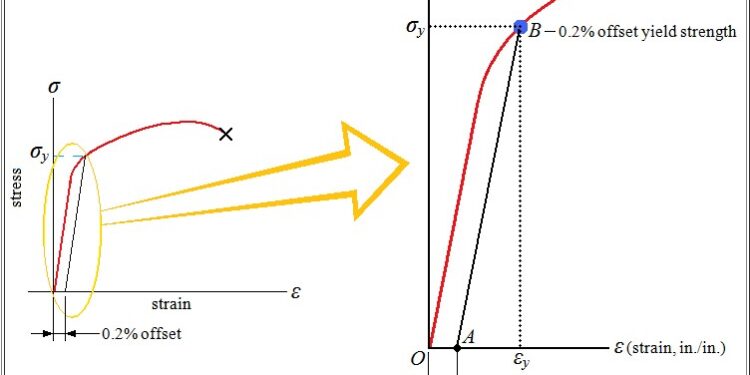
0.2 offset yield strength is a vital concept in stress measurement. Read further to understand why this method is essential while measuring yield stress.
Types of Deformation
When loaded, two types of deformation happen to a material- elastic and plastic. In both situations, some physical changes occur to the material concerned. However, it differs according to the weight and capacity of the stress applied to it. Here are the details:
- Elastic– It is a temporary deformation that occurs to the material due to the application of stress. However, the material regains its original form and structure as soon as the stress is removed. The deformation disappears as soon as the stress disappears. Therefore no such harm is caused to the material. It occurs in ductile materials which have a high resistance strength.
- Plastic– It refers to the permanent deformation that happens to the material. It may lead to a crack, Hardening, fracture, or necking of the material. Hooke’s law measures the amount of elastic deformation that has occurred and its direct effect on the material concerned.
What is the 0.2 Offset Method for Yield Stress?
When deformation occurs in a material, it becomes difficult to understand the nature of the changes. In simple words, it becomes tough to know whether it is elastic or plastic deformation. In this case, the 0.2 offset yield strength is taken into account.
It refers to the stress value distinguishing between the elastic and plastic regions. It is also called proof stress and is denoted as R_p0.2.
The material suppliers often mention the 0.2 offset yield strength value in the material details. In the case of fragile materials, it can range from 0.05 to 0.1% because the plastic deformation is negligible.
It varies from material to material and requires accurate measurements to better present the yield stress value. While understanding deformation, you must be careful about the slide changes in the following measurements.
Conclusion
The 0.2 offset yield strength is a vital concept in measuring deformation, especially when you cannot determine whether it is elastic or plastic deformation. The difference is minimal that can only be measured with the help of yield stress value.
Engineers who clearly understand the offset yield strength value will have a better approach when measuring deformation, mainly because of the immense vague concepts that follow.
Yield stress measurement has a number of critical concepts that you must understand so that you can experiment with the expansion methods and bring out accurate results as and when necessary.