A prism has a solid refracting medium, with two plane surfaces inclined at an angle. Based on the application of the prism, they are made in different shapes. Triangular prisms are the most commonly used prisms. A prism is generally made using glass, or other transparent material, and is cut with precise angles.
Prism
As light enters the prism, the speed of light changes and causes refraction. This causes the light to enter the new medium at a different angle. The degree of bending of the light as it passes through the prism depends on the refractive index of the prism, and the angle of incidence of the light with the surface. White light consists of seven colours. The refractive index of the medium used in the prism changes with the wavelength or colour of the light used. This phenomenon is called dispersion. If the light hits the prism at a sufficiently steeper angle, then there is total internal reflection.
What is Refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light rays when they travel from one medium to another. When the lower half of a pencil is dipped in a glass of water, the portion of the pencil inside the glass of water will look bent, due to refraction.
Refraction of light is explained by Snell’s law of refraction. According to Snell’s law,
n1sin θ1 = n2sin θ2
Here, n1 is the refractive index of the medium from which the light ray is incident.
n2 is the refraction index of the medium refracting the light
θ1 is the angle of incidence
θ2 is the angle of refraction
Refractive Index
The refractive index is the property of the material, the value of the refractive index will be different for different materials. When light rays travel from a vacuum to any other medium, the speed of light slows down. The light travels slower if the medium is denser. The speed of light in a vacuum is denoted by the letter c, and the refractive index of the medium is denoted by n. The speed of light in any medium can be written as
v = c/n.
The speed of light in the vacuum is equal to 3 x 108 m/s.
Types of Prisms
Prisms are mainly of four types, namely dispersion prisms, displacement prisms, deviation prisms and rotating prisms. In a dispersion prism, there is a dispersion of light rays. The deviation prism deviates from the path of light, the rotating prism rotates the image and the displacement prism displaces the image from the original axis.
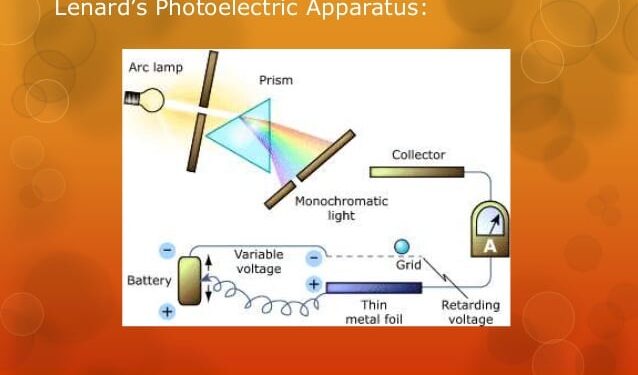
To learn more about physics topics like “Photoelectric Effect”, visit BYJU’S pages. The photoelectric effect is the phenomenon of releasing electrons from the surface of the material when electromagnetic radiation hits the surface of the material. The electrons that are released during the process are called photoelectrons. The properties of the photoelectrons are the same as that of the electrons. The photoelectric effect leads to the dual-nature concept of electromagnetic waves.